Definition
Cancer is an aggressive growth disorder initiated by a cell or a group of renegade cells with genetic aberrance, usually caused by either a carcinogen in the environment, or less commonly by an inherited genetic aberrance. Cancer is characterized by rebel type characteristics, with squatter type existence in the host organ, occupying space, with independant growth, parasitization of nutrition and oxygen, but without contributing to the overall function of the mother organ or to the community at large.
The structural changes are characterized by aberrant non functioning space occupation of tissue with a variety macroscopic morphologies, but often characterized at a cellular level by large hyperchromatic nuclii with diminished cytoplasm.
Occasionally they have aberrant functionality but more characteristically have only a destructive nature on the function of the mother organ and the body.
The disease is complicated by local spread within the organ and surrounding tissues, displacing well meaning and well functioning tissue. Continued uncontrolled growth results in the invasion of blood vessels and lymphatics and spread to distant organs where metastatic disease repeats the pattern of continued advance of rebellious parasitization on normal tissue.
The diagnosis is suspected clinically when unexplained weight loss in an older patient is a presenting symptom ar a new mass is felt on clinical examination. Imaging characteristics include finding a mass, characteristically with a spiculated appearance, that shows evidence of local invasion and metastatic pattern. PET scan is able to characterize the metabolic pattern of disease, and cancer typically is hypermetabolic. When cancer is suspected, pathological confirmation is universally indicated to confirm the diagnosis, and to evaluate and classify the type and virulence of the cancer. Staging the disease is essential since treatment plans depend on the staging.
Treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Recent advances include localized chemical ablation with alcohol for example, or thermal or elctrical ablation.
Etymology if available
Principles
Malignancy
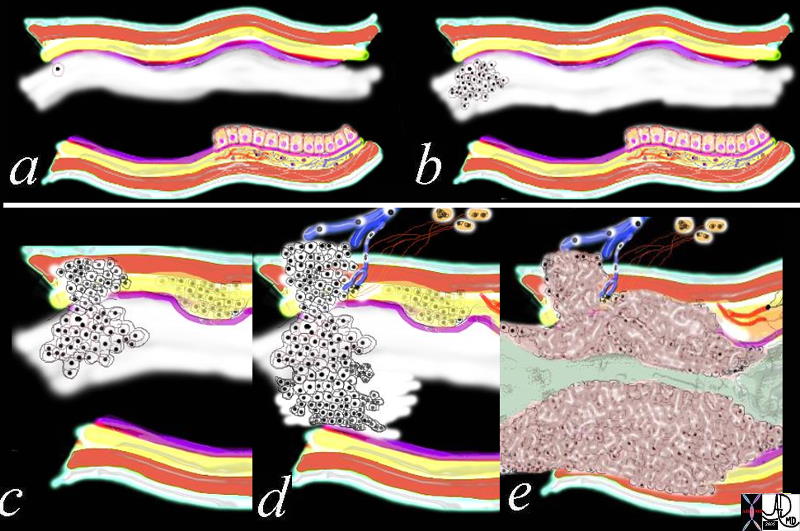 Growth of a Malignancy Growth of a Malignancy |
| 32354c01.800 tube colon trachea bronchus small bowel bile duct epithelium neoplasm benign malignant malignancy epithelial cell multiply multiplication growth mucosa submucosa muscularis serosa adventitia vein lymph node circumferential metastasixe metastasis metastases narrowing stenosis obstruction complication cancer uncontrolled growth Davidoff drawing Davidoff art Davidoff tube Davidoff MD |
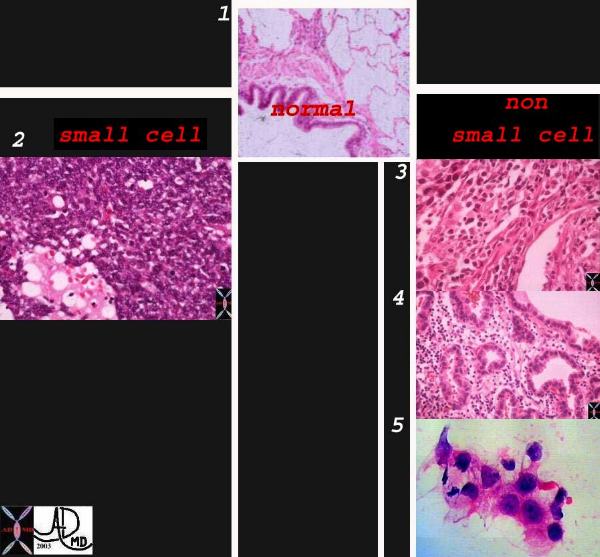 Classification of Lung Carcinoma Classification of Lung Carcinoma |
| Classification system of carcinoma of the lung based on histological subtype. This collage of histopatholgy images of lung carcinoma shows part of a normal bronchiole and a few alveoli (1), followed by a small cell carcinoma (left lower 2) and non small cell carcinoma grouped together on the right side with squamous cell(3), adenocarcinoma with glandular formation (4), and undifferentiated large cell derived from pleural aspirate (5). 1-4 Courtesy Dr Armando Fraire MD, and image 6 courtesy of tumorboard.com 32501cL02.jpg code lungs pulmonary neoplasm primary malignant malignancy small cell carcinoma non small cell NSCC classification histopathology |
The Faces of Malignancy – Occupying Space
Size and Doubling Time
 Growth of a lung lesion over 7 months Growth of a lung lesion over 7 months |
| 48380c01 chest lung fx mass fx growth in 7 months dx metastattic squamous cell carcinoma head and neck primary primary larynx metastasis time size CTscan Davidoff MD 48383c01 48380c01 48383c02 malignant malignancy |
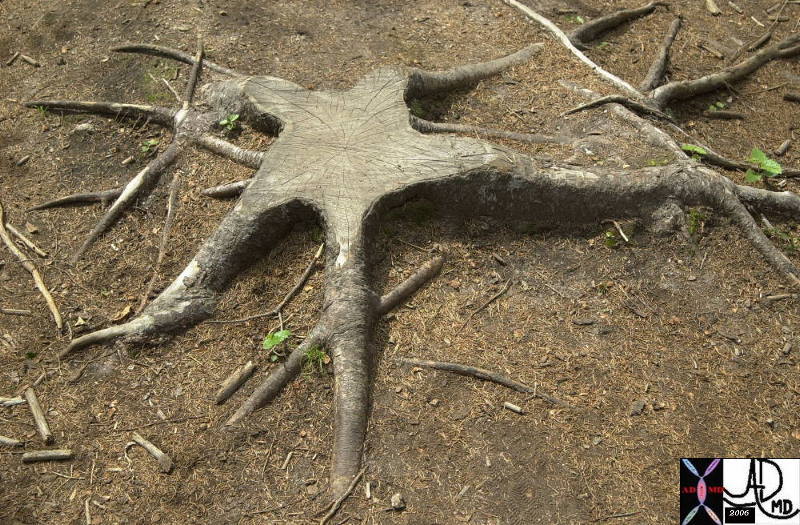
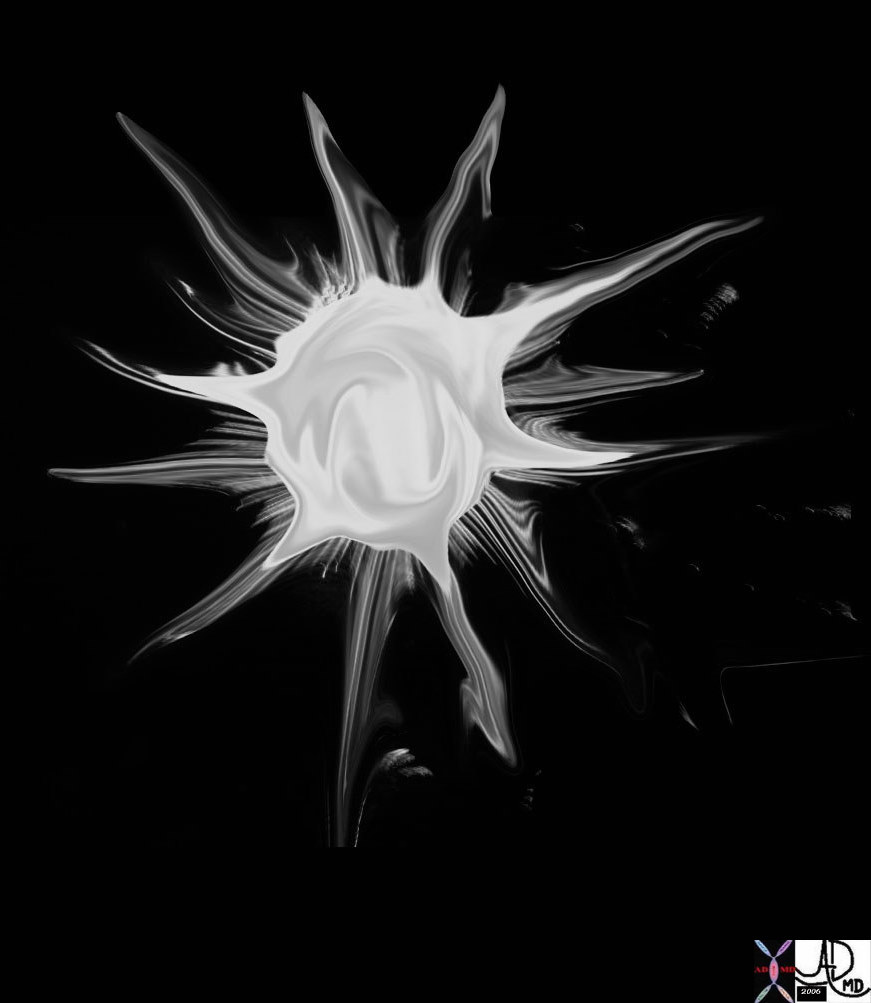

 Shape – Spiculated Masses
Shape – Spiculated Masses
| Stellate |
| 69595b05.800 Davidoff art star stellate corona radiata spiculated aggressive cancer carcinoma
70142.800 tree roots stellate shape Davidoff photography New Hampshire 46361b01 lung fx spiculated nodule dx carcinoma CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
 Spiculated Lung Nodule Spiculated Lung Nodule |
| 46361 lung fx spiculated nodule dx carcinoma CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
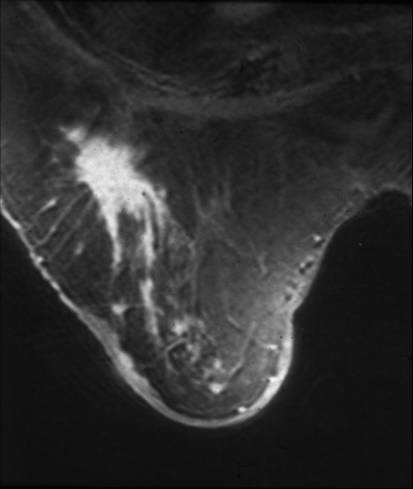 Spiculated Mass in the Right Breast Spiculated Mass in the Right Breast |
| This is an MRI of the right breast of a 78 year old patient with a remote history of invasive lobular carcinoma. The finding on the MRI is characterized by an enhancing spiculated mass. Recurrent carcinoma was present at pathology. Courtesy Priscilla Slanetz MD MPH 42977 |
Ulcers
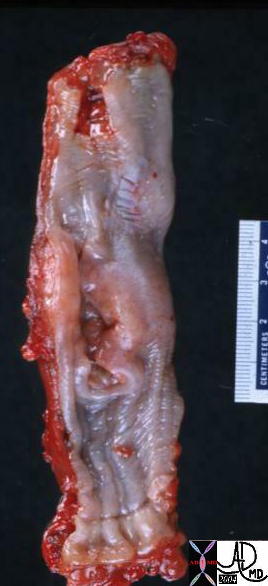 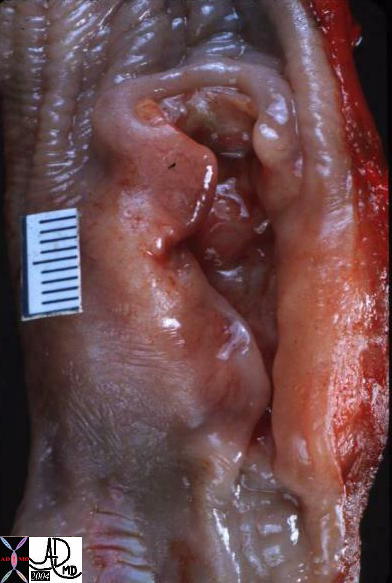
Ulcerating Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus |
| 02425 02420 code esophagus + mass narrowing stricture ulceration heaped edges squamous cell carcinoma + grosspathology |
Malignant Progeny
Position –
Space Occupying
 Squatters in the Left Lobe Squatters in the Left Lobe |
| 46587.800 liver bone vertebra fx mass space occupying disease dx liver metastases metastasis dx primary lung carcinoma malignancy cancer CTscan Davidoff MD |
Character
 Small arterial fed liver lesion Small arterial fed liver lesion |
| 48369c03 40 male with hepatitis B liver fx hypervascular lesion seen in early arterial phase only with rapid wasout dx HCC hepatoma hepatocellular carcinoma capillary hemangioma characterisation characterization blood flow CTscan MRI Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD |
 Malignant Neoplasm Cystic and Solid Componenets Malignant Neoplasm Cystic and Solid Componenets |
| 49484c02 brain cerebrum possterior aspect calcarine fissure posterior medial occipital lobe fx mass cystic fx mural nodule fx intraaxial fx calcification calcified dx neoplasm neural tumor or mixed neural glial tumor or pilocytic astrocytoma MRIscan T1 minimally enhancing FLAIR hyperintense T2 cystic and solid components MRI GRE Davidoff MD |
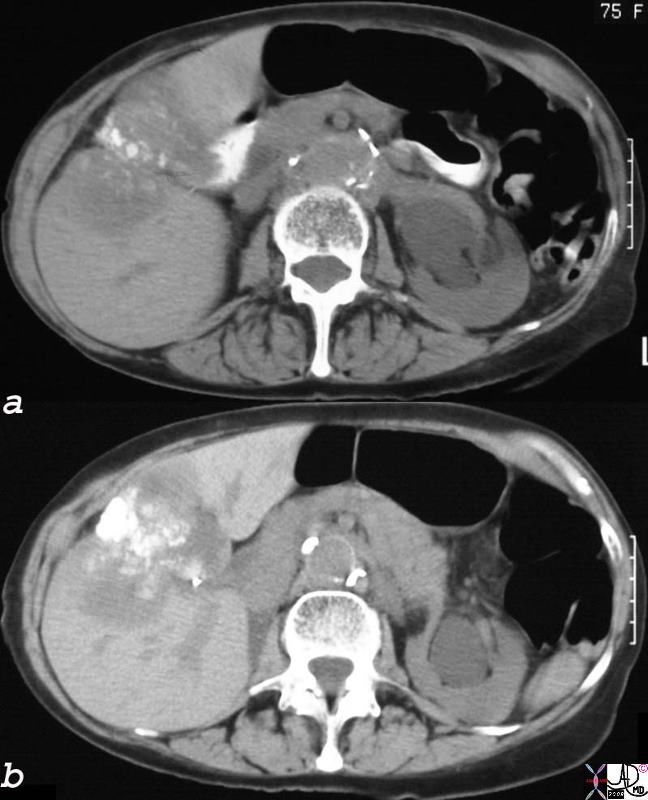 Dystrophic Calcification – Carcinoma of the Gallbladder Extending into the Gallbladder Fossa Dystrophic Calcification – Carcinoma of the Gallbladder Extending into the Gallbladder Fossa |
| 24404c.8s 75 female gallbladder calcification adjacent mass in the liver local invasion into the gallbladder fossa dystrophic calcification probably mucinous adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder carcinoma stones cholelithiasis hydronephrosis |
Infiltrative Malignancy
  Infiltrative Adenocarcinoma of the Lung Infiltrative Adenocarcinoma of the Lung |
| 46588 46581 lung fx consolidation dx adenocarcinoma of the lung malignancy cancer Davidoff MD |
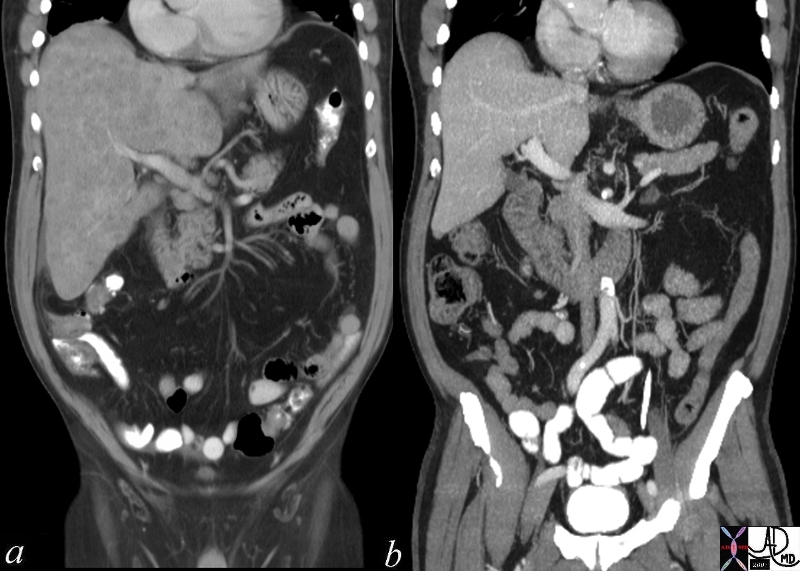 Chemotherapy – Before and 6 weeks After – Metastatic Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Chemotherapy – Before and 6 weeks After – Metastatic Small Cell Lung Carcinoma |
| 70248c01 liver metastattic small lung carcinoma with diffuse metatstattic disease to the liver )hepatic metastases metastasis before and after treatment 6weeks post chemotherapy successful result size change character change CTscan Davidoff MD 5star |
Calcification
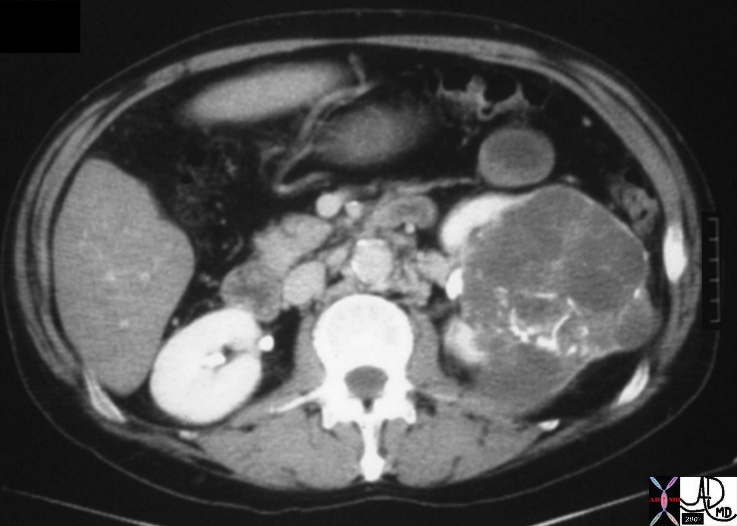 Cystic Renal Celll Carcinoma Cystic Renal Celll Carcinoma |
| 05730.800 kidney renal mass fx coarse calcifications curvilinear linear calcified space occupying displacement cystic enhancing septations dx cystic renal cell carcinoma RCC CTscan Davidoff MD Bosniak grade 4 05730.800 05730b.800 05729b |
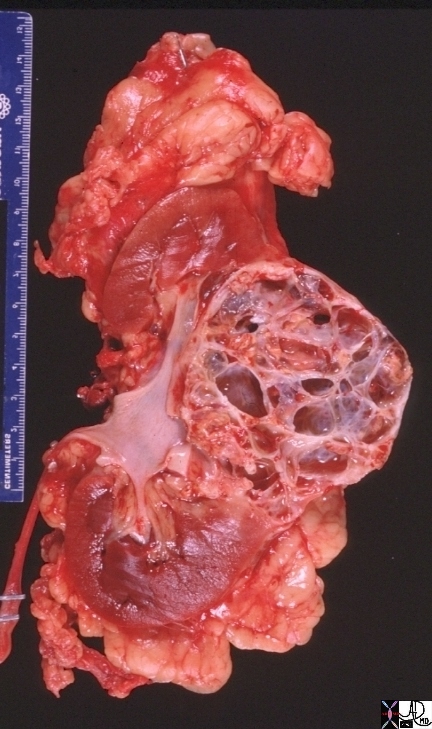 Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma |
| 05729b kidney renal mass space occupying displacement cystic dx cystic renal cell carcinoma RCC grosspathology CTscan Davidoff MD Bosniak grade 4 05730.800 05730b.800 05729b |
Neovascularity
 Neovascularity of Renal Cell Carcinoma Neovascularity of Renal Cell Carcinoma |
| 48107c01 kidney renal mass large cystic mass 2cms solid mass with hypervascularityhypervascular mass suggestion of arteriovenous shunting AV shunting large feeding arteriole and large draining vein dx renalcell carcinoma USscan Davidoff MD
|
Malignancy – Vascular Invasion
 Vascular Invasion Vascular Invasion |
| 46579 liver hepatic vein fx tumor thrombus lung fx consolidation dx infiltrative adenocarcinoma of the lung with metastases to the liver and adrenal and invasion of the hepatic veins malignancy cancer Davidoff MD 46581 46588 46587 |
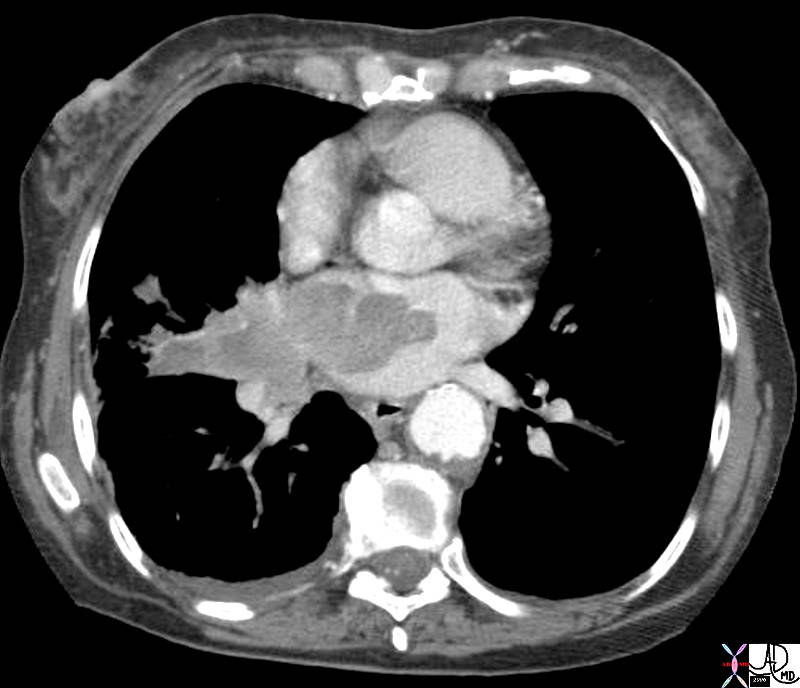 Lung Cancer Invading the Left Atrium Lung Cancer Invading the Left Atrium |
| 42379.800 heart cardiac pulmonary veins LA left atrium fx mass dx lung carcinooma invading the left atrium CTscan Davidoff MD space tumor aggressive space |
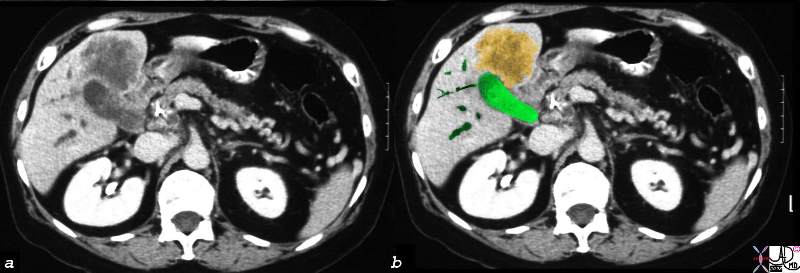 Direct Invasion into the Liver and Bile Duct Obstruction Direct Invasion into the Liver and Bile Duct Obstruction |
| 16254c02b.8s gallbladder anterior wall liver invasion space occupatopn obstruction bile ducts aggressive gallbladder carcinoma complicated by direct invasion metastasis liver windows narroe windws tumor settings gallbladder fossa GBF CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff copyright 2008 |


Malignancy – Vascular Encasement
| Vascular Encasement |
| 46645c03.800 46645c04.800heart artery pulmonary trunk encasement right ventricle RV infundibulum dx carcinoma of the lung CTscan Davidoff MD |
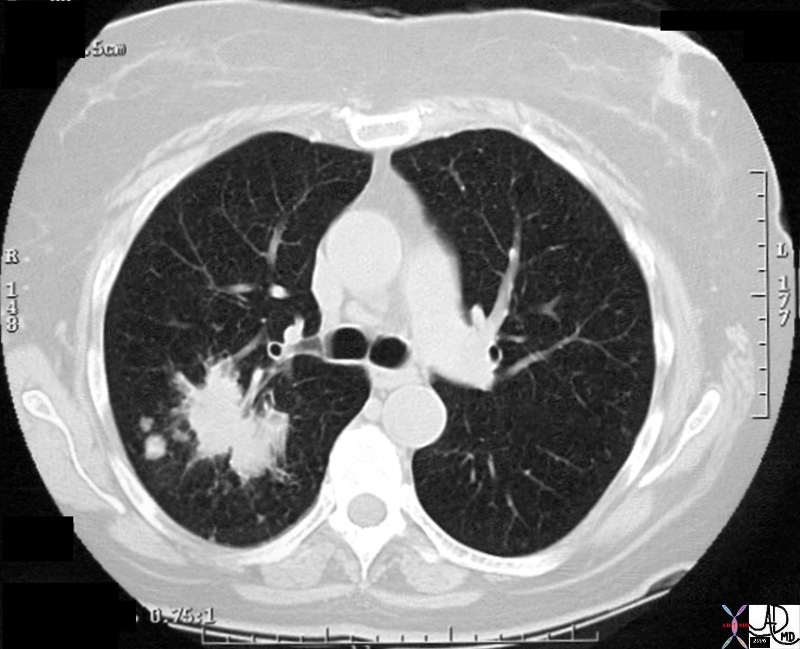 Satellite Nodules Satellite Nodules |
| 28980 chest lung spiculated mass satellite nodules malignant carcinoma CTscan Davidoff MD 28979 28980 28981 28984 28985 28986c01 |
|
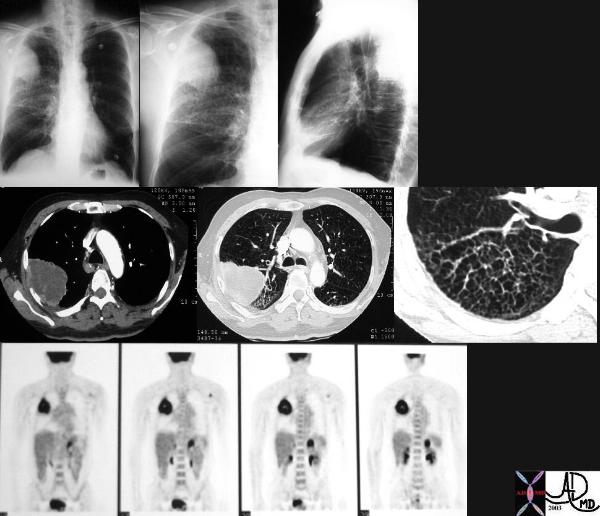
Stage 4 |
| This is a patient with lung carcinoma presenting with a large mass in the right upper lobe with a lymphangitic pattern, adrenal metastasis and a PET positive scan for the mass and for the left adrenal gland.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 32269b see 680249 |
Weakening of Tissues
 Pathological Fracture Pathological Fracture |
| 49471c03 bone hx male with history of metastatic lung carcinoma bone femur femoral neck fx fracture fx osteolytic bone lesion in neck dx pathological fracture artery atherosclerosis CTscan Davidoff MD 49471c032 |
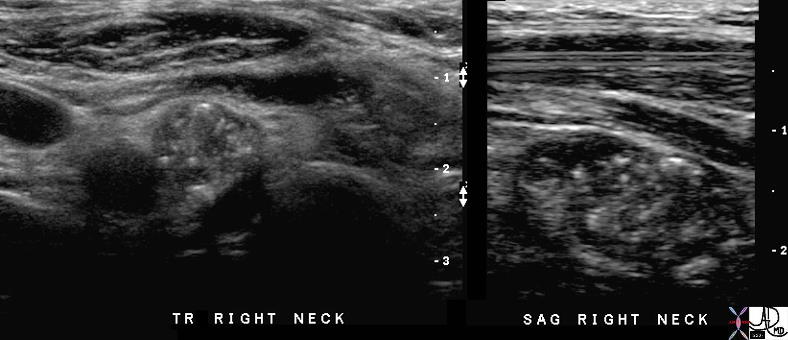 Calcified Thyroid Metatstases in Lymph Nodes Calcified Thyroid Metatstases in Lymph Nodes |
| 70982c01 lymph nodes cervical thyroid bed calcifications punctate shadowing lymphadenopathy papilllary thyroid carcinoma recurrence after 16 years USscan Davidoff MD |
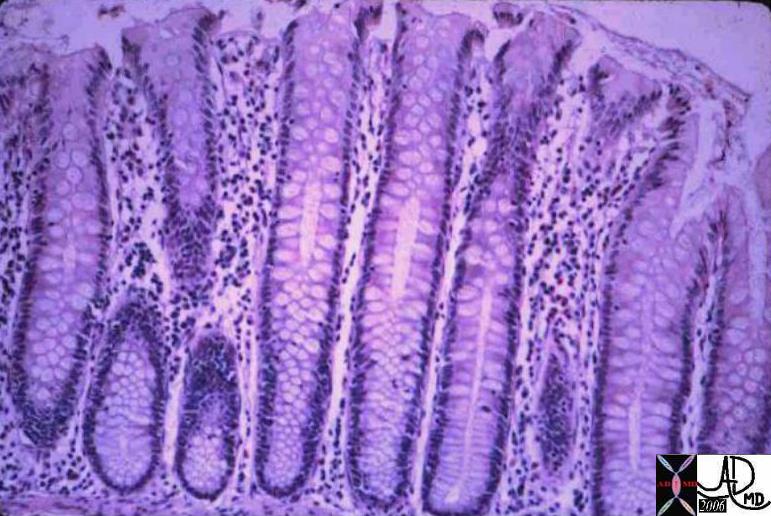 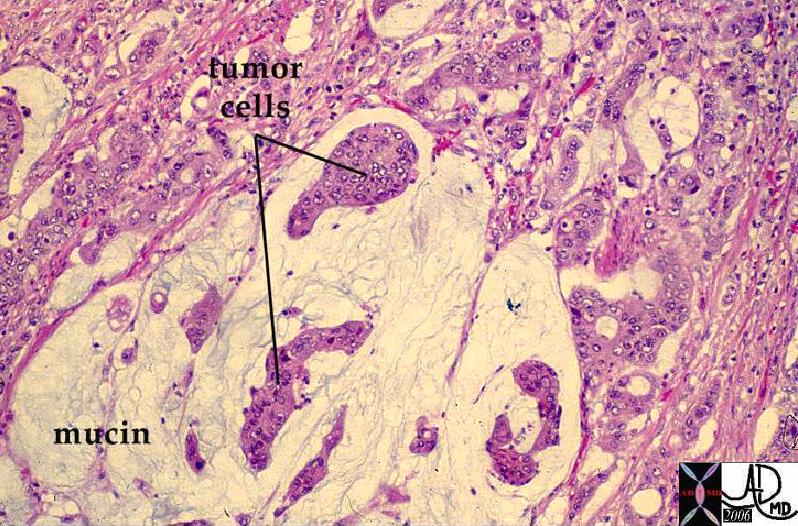 Normal Colonic Mucosa (right) and Mucin Secreting Colon Carcinoma (left) Normal Colonic Mucosa (right) and Mucin Secreting Colon Carcinoma (left) |
| The image on the right shows the normal crypts while the left image shows a mucin secreting adenocarcinoma. The most obvious difference between the two images is the nuclear cytoplasmic ratio. Note in the case on the right, the cancer nuclii are large and heterogeneous while there is a relative paucity cytoplasm.
12860 12208 colon large bowel fx mucin secreting fx mucinous accumulation dx carcinoma mucin secreting adenocarcinoma histopathology Courtesy Barbara Banner MD ask |
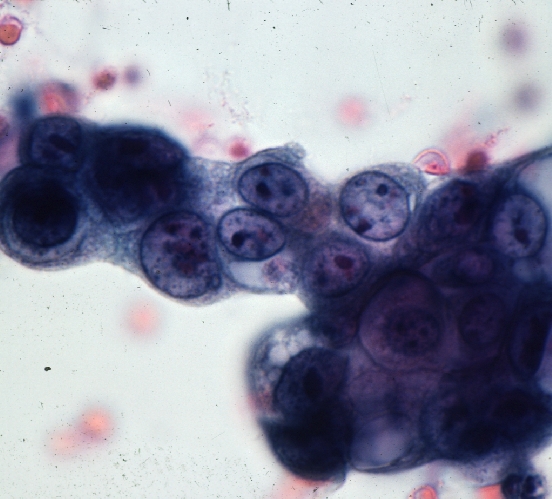 Colon Carcinoma – Cytopathology Colon Carcinoma – Cytopathology |
| These cells represent a group of malignant cells characterized by large heterogeneous nuclii with a high nuclear cytoplasmic ratio.
44834 colon large bowel dx carcinoma mucin mucinous histopathology cytopathology Courtesy Barbara Banner MD ask |
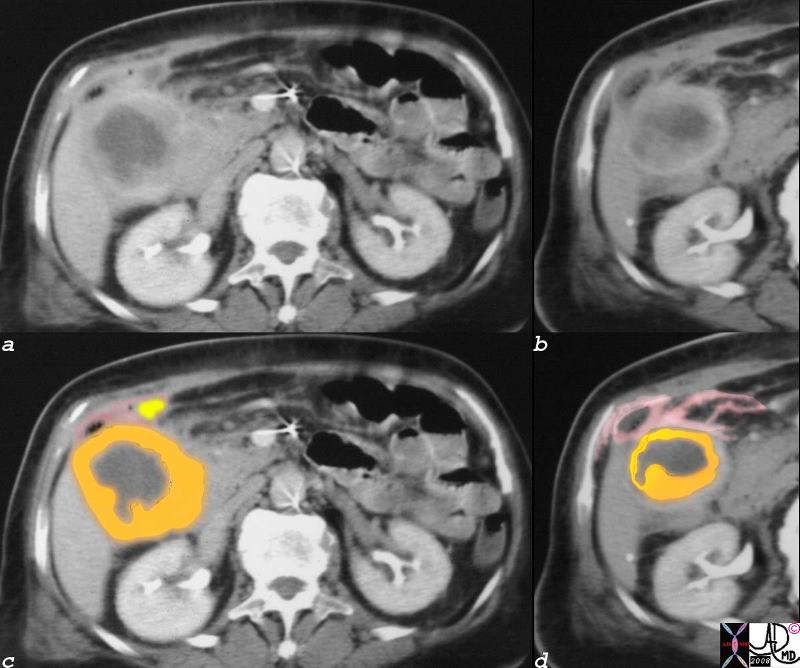 Gallbladder Carcinoma with Perforation and Abscess Formation Gallbladder Carcinoma with Perforation and Abscess Formation |
| 16254c01b02.8s gallbladder thickened irregular wall air anterior wall small fluid collection gallbladder carcinoma complicated by perforation and abscess formation CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff copyright 2008 |
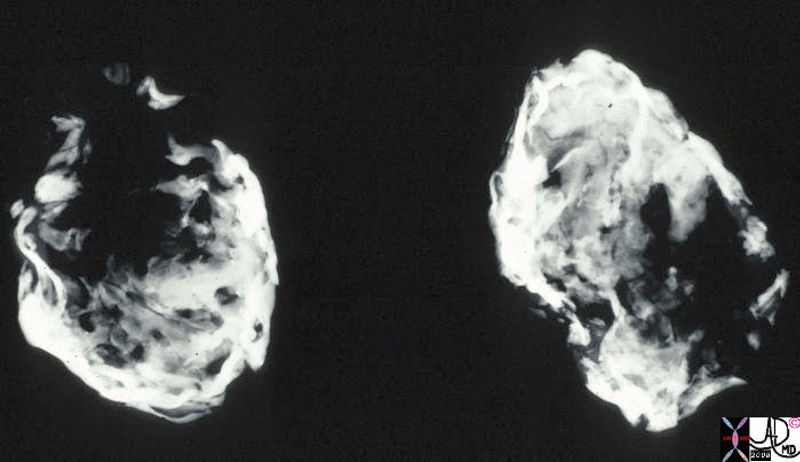 Porcelain Gallbladder – Variant of Chronic Inflammation Porcelain Gallbladder – Variant of Chronic Inflammation |
| This is a specimen xray of a resected gallbladder. The walls were thin, fibrotic and heavily calcified, accounting for the radiodense (white) areas on the radiograph. This variant of chronic cholecystitis is a risk factor for development of carcinoma.
11939.8s gallbladder porcelain gallbladder X-ray Courtesy Barbara Banner MD |
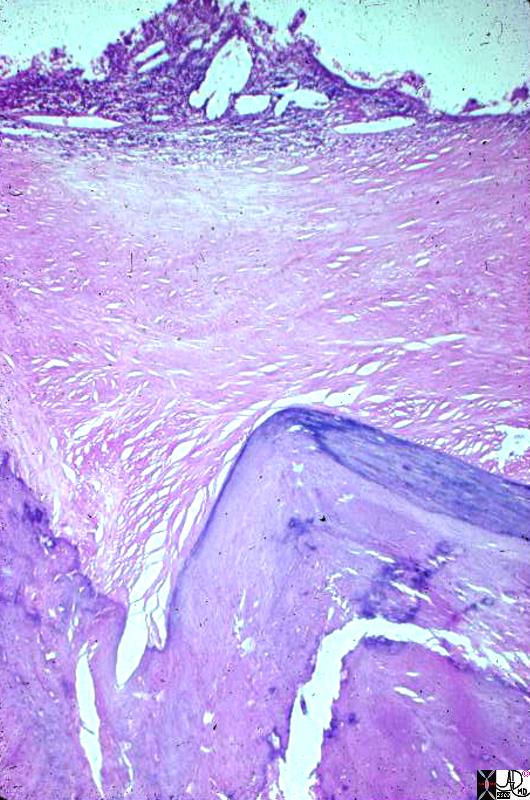 Porcelain Gallbladder – Variant of Chronic Inflammation Porcelain Gallbladder – Variant of Chronic Inflammation |
| This photomicrograph at low power shows most of the full thickness of the wall of a gallbladder. The lumen is the clear area at one side of the picture. The pale homogeneous area down the middle is fibrous replacement of the wall. The little nubbin of tissue and cholesterol clefts along the lumen represents what is left of the mucosa. The darker, zig-zag structure at the side opposite the lumen represents where the gallbladder wall is calcified. This calcification and fibrosis of the entire gallbladder wall is the diagnostic feature of porcelain gallbladder.
11940.8s gallbladder porcelain gallbladder histopathology Courtesy Barbara Banner MD |
Malignancy and Time
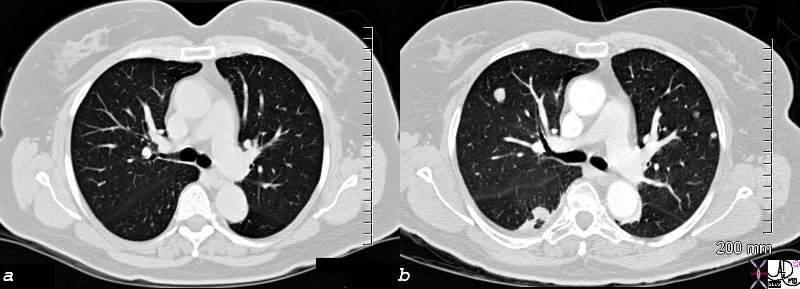 Sarcoma Chest CT – 2 months apart Sarcoma Chest CT – 2 months apart |
| 82435c01.8s 58F with diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma of the uterus presents 6/25/08 with a single lung nodule in the right lower lobe and a large uterine mass 2 months later she has innumerable nodules in the lung a mass in the right neck This is an example of raptidity of growth uncontrolled malignant growth lung metastasis CT scn Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 a = 6/25/08 b = 8/27/08 |
 Malignant Disease in the RUL with PET positive Left Adrenal Gland –
Malignant Disease in the RUL with PET positive Left Adrenal Gland –